Examples
P-glycoprotein
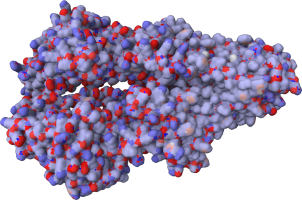
P-glycoprotein is part of the ABC transporter proteins that decrease drug accumulation in cancer
cells (Leslie2005).
It is a 170-kDa protein which consists of a nucleotide-binding domain and a transmembrane domain
(Ward2013).
Partial atomic charges calculated by
αCharges
demonstrate the differences in charge
distribution between transmembrane parts and the extracellular/intracellular one.
Pepsin
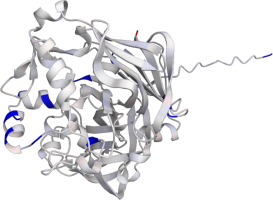
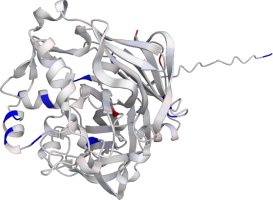
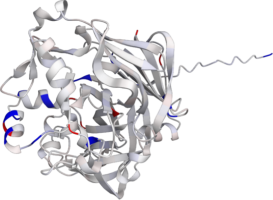
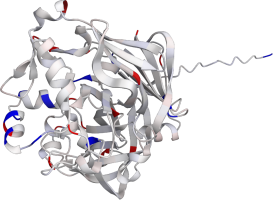
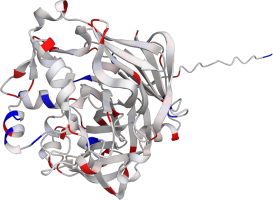
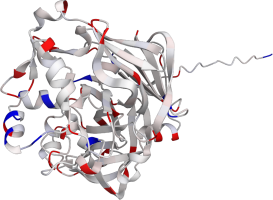
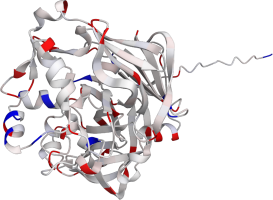
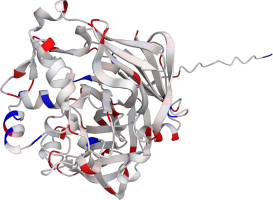
Pepsin is the enzyme that is majorly involved in protein digestion in the stomach. It is secreted
as a zymogen and activated by the acidic pH created by the stomach parietal cells. Pepsin is the
most effective at a pH of approximately 1.5 to 2, and it becomes inactive when the pH rises above 6
(Heda2022). Pepsin remains structurally stable until at least a pH of 8.
Differences in a charge distribution between its active form (pH 2) and inactive form (pH 8) can be
seen in this use case. The alkaline environment causes an increase in negative charges, which
contributes to the structural instability of the pepsin, causing the shift to an inactive form of
the protein (Tanaka2001, Grahame2021).
PIN proteins
The PIN family proteins control plant growth by regulating auxin export from the cytosol to the
extracellular space. Eight types of PIN proteins are known (PIN1-PIN8), and last year, structures of
three of them were discovered and published in Nature (i.e., articles about
PIN1,
PIN3,
PIN8).
Partial atomic charges play an important role in PINs functionality.
The PIN protein part inside the cytosol (containing the cytosolic loop) is charged more than the
part outside the cytosol. Questionable is the charge distribution of PIN5, which structure differs
from other PINs (Ung2022) and was not experimentally determined yet. In the
use case, you can compare the charge distribution of AlphaFold2 predicted PINs from A.
thaliana.
If you found
αCharges helpful,
please cite:
Schindler, O., Berka, K., Cantara, A., Křenek, A., Tichý, D., Raček, T., & Svobodová, R. (2023).
αCharges: Partial atomic charges for AlphaFold structures in high quality.
Nucleic Acids Research.
Are you interested in a research collaboration? Feel free to
contact us.

αCharges tool is
a
part
of services provided by
ELIXIR
–
European research infrastructure for biological information.
For other services provided by ELIXIR's Czech Republic Node visit www.elixir-czech.cz/services.
For other services provided by ELIXIR's Czech Republic Node visit www.elixir-czech.cz/services.
Licence conditions in accordance with § 11 of Act No. 130/2002 Coll. The owner of the software is Masaryk
University, a public university, ID: 00216224. Masaryk University allows other companies and individuals to
use this software free of charge and without territorial restrictions in usual way, that does not depreciate
its value. This permission is granted for the duration of property rights. This software is not subject to
special information treatment according to Act No. 412/2005 Coll., as amended. In case that a person who
will use the software under this licence offer violates the licence terms, the permission to use the
software terminates.